Understanding Scrum & its Components
Scrum is among one of the most popular agile methodologies. Software development teams prefers to use it. The main focus of Scrum is to make the project management activities effective.
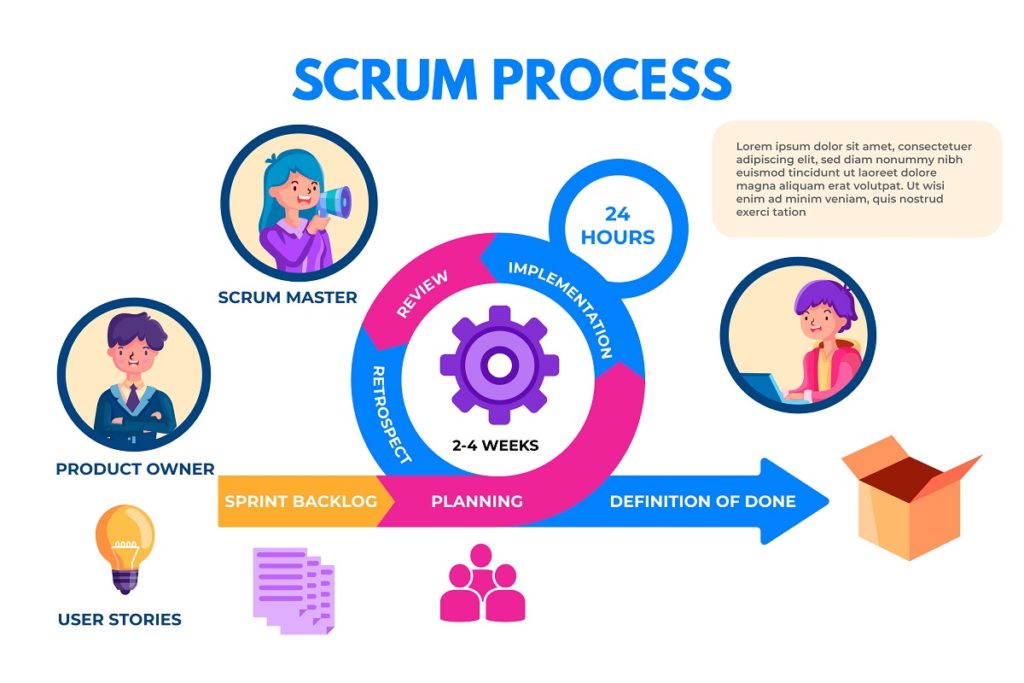
There are three basic pillars of Scrum: visibility, adaptation and inspection. Scrum consists of different ‘sprints’, which contain the user stories and range from 1 to 4 weeks.
Who Uses Scrum Methodology?
70% of the software teams use Scrum or Scrum Hybrid as per a report published by State of Agile. Scrum has spread to different business capacities including IT and showcasing where there are projects that must push ahead within the sight of unpredictability and uncertainty.
The management-related team is likewise putting together their agile management practices on Scrum, frequently consolidating it with lean and Kanban practices.
The major components of Scrum or Scrum events are as follows:
1- Sprint Planning
Sprint planning usually consists of two meetings which held on very first day. The product owner conducts the first meeting. And he arranges the user stories and explains them to the team.
After that, the team selects those user stories for sprints. The scrum master conducts the second meeting. And he assigns the user story tasks to the team.
2- Daily Scrum
The scrum master conducts a daily meeting with the development team for 15 minutes. And ask following questions from each member of the team:
- What have you done since the last meeting?
- What will you do next?
- Any problems that you are facing?

3- Sprint Review
This meeting is conducted after every sprint to showcase which new functionalities which are developed in that particular sprint.
4- Sprint Retrospective
It is different from the sprint review. The scrum master conducts this meeting at the end of every sprint, in order to understand three points.
- Things that are right?
- What’ was wrong?
- What should we do?
This is one of the most popular agile methodologies and it helps in understanding the activities in much better way.
What Are the other Components of Agile Scrum Development?
The scrum team normally consists of three to nine teammates. There is no lead available for task assignment. The team as a single unit decides how to address issues and solve them.
There are three key roles in a Scrum team:
The Product Owner
The most important stakeholder of a project is the product owner. A customer itself, spokesperson of a customer. There is only a single product owner who answers questions and queries of the dev team. And the product owner is also known as a project backlog manager.
The Scrum Master
They are the junior of product owner and works as a facilitator between the development team, an organization he works in, and the product owner. The scrum master helps the development team to perform at the highest level by doing meetings, grooming backlog, etc.
The Development Team
The development team is the workforce of engineers and developers who are building software, in simple words developers or programmers.
What are the scrum artifacts?
Product Backlog
Every project consists of number of backlog items which are outlines of every requirement for system development and this is used to make a to-do list for workable items. Backlog items are requested as per requested by the Product Owner.
Sprint Backlog
A sprint backlog is the specific list of features taken from the product backlog which are required to be finished in a sprint.
Increment
When all of the product backlog features are completed. Then product owner releases an increment before the main software release. Increment is also called Potentially Shippable Increment (PSI).
Benefits of Scrum Methodology?
- Higher productivity
- Better-quality products
- Reduced time to market
- Improved stakeholder satisfaction
- Better team dynamics
- Happier employees
What should a Scrum Master avoid from doing?
It is not acceptable for the Scrum Master to play politics. In a quarrel, the Scrum Master’s facilitator position means that he would always not take sides or get a preference for someone’s viewpoint.
Therefore, he should act as a connector between the clients, assisting them in reaching an agreement.
What difficulties does a Scrum Master face?
1. Time-boxing is harder to manage.
The Scrum Master is in capable of ensuring time-boxing of tasks on Daily basis. Team members who are not allowed in this timeframe are unable to perform their work.
Time-boxing is used to set the upper limit of timeframe for each event and activities. And the groups which are not bound to this runtime are unable to perform their work.
Participants who aren’t paying attention can ruin the session, so if the Scrum Master doesn’t keep the needed attention in control, there will be huge delays.
The solution:
Keep every meeting’s agenda clear, highlighting the significance of proper time-boxing, and tell anyone who goes off as well their problems may be handled separately because the team having time is important.
2. The Scrum Master’s responsibility is regarded as optional.
Let’s be clear about something. The Scrum Master may not be the team’s manager or director. He or she is a valuable member who facilitates and encourages working while also removing roadblocks to smooth development.
The solution:
Instead of working above the team, the Scrum Master have to get down and dirty and working with among them. Somebody who is familiar with the agile methodology, you are asked to make the team’s travel as easy as possible.
3. A lack of senior management buy-in
Agile is a concept that must be adopted by the entire organization, not just a few individuals. When senior management does not truly appreciate the effort, the rest of the team may suffer.
The solution:
What could be performed to get around it? Rather than explaining why senior management should take Agile, check out what their issues are and fix it using an agile approach. They’ll soon follow in their footsteps while becoming agile supporters.
4. Incorrectly handled Agile Meetings
Often people seem to believe that meetings are a waste of effort, particularly when they’re not adding to the talk. Group meetings, on the other hand, are required to get the entire team in place with agile values of visibility and assessment to work out the way they can.
Basic Agile meetings are brief but extremely valuable since they allow the team to discuss, overcome obstacles, and organize for the work ahead.
The solution:
Scrum Masters should keep all meetings on schedule, provide value to all participants, and optimize the team’s quality and performance.
5. There’s a competition between Agile and Waterfall.
This occurs more frequently than you might expect. Experienced team members who’ve already traditionally used the Waterfall technique may understand the agile methodology, however, find it extremely difficult to put them into practise.
This is one of the most common reasons why agile transformations fail, and firms who try to go Agile usually run into disagreements, misunderstandings, ego problems, and a loss of trust in the approach.
The solution:
A skilled Scrum Master would gently explain the benefits which have been achieved and share information on agile Working shipping orders to have everyone on platform with Agile.
Staff members can be encouraged to join the stronger candidate by clearly displaying the benefit that will be received.
6. Improper Agile Training
Agile techniques are simple to understand but challenging to implement. Until your staff members understand the basic principles of agile, they will not engage enough with the system and addresses the root of an issue.
Being on the same page, they must have a basic awareness of agile terms and techniques.
The solution:
If somehow the team is unfamiliar with Agile, as nothing more than a mentor, you will need to teach them and bring them up to full speed on Scrum.
7. Stakeholders and Agile Teams don’t connect well.
Agile teams may have the skillsets to adopt Agile to a letter, people viewing as stakeholders, providers, some do not have a strong idea of what it means to be Agile.
The solution:
It is critical that they know how such iterative approach performs and are committed to supporting review at times in order to connect with your new ways of doing things. You might bring them to several planning meetings so that they will be knowledgeable.
8. Addressing Scope Changes
Although it is the Product Manager’s role to oversee the scope and objectives of the project, the PO could only go there with the help of the Scrum Master.
When new project is presented at the organization at randomly, or they will be requested to make a different choice, they may become very confused.
The solution:
They must communicate with the Vendor to collect input on a regular basis that will allow the team members de-clutter and gain understanding.
9. Relationship with the Product Owner is Unhealthy
Scrum Master and Product Owner are two sides of same coin. They communicate for the greater good of everybody. However, they frequently have personalities that clash, resulting in a breakdown in communication that impedes work progress.
The solution:
Even if there are little disagreements, the Scrum Master and Product Owner would work together to fix issues before they are a filled miscommunication.
For such team’s overall health, a friendly connection with enough mutual exchange is required.
10. Scrum Master Assumes Admin Responsibilities
They are required to arrange meetings, do the planning for events and do follow ups. While they may be the perfect person that takes on this task, this will not take away from the Scrum Master’s work duties.
The solution:
The core purpose of the Scrum Master is to facilitate teamwork, and any additional activities should not affect from this. To make sure the project is checked by you, try to assign administrative responsibilities and be a great communicator.
11. Handling distributed teams
For a Scrum Master, distributed teams present a completely series of problems. Lots of people work across multiple time zones, geographical concerns, or connectivity issues, there may be difficulties in today’s world of remote work and distributed teams.
The solution:
They might have difficulties when working with such team members, but they may overcome these challenges by utilizing technology and communicative tools.
12. The Fear of Transparency
Many individuals who already have performed in the Waterfall approach are slow to accept more accessible work procedures. Senior management is comfortable with having dominant positions, which might be a challenge to agile methodologies, which do not have a highest architecture.
The solution:
They must observe where top management visibility is required or necessary. Managers with transparency into these aspects can make well-informed choices that will improve both team performance and organizational success.
13. Single vs. Team Performances
The Scrum team must work as a unit to achieve aims instead of focusing on individual value creation. When group members aim for self – improvement rather than working together as a solid one, this can lead to delays in development. Whenever a corporate policy encourages individuals over teams, the situation becomes even worse.
The solution:
HR must inform agile team about how much overall performance is important. They should consider personal opinions as well.
14. Management Expectations are varying
When there is a major disagreement among management on what is the most essential objective, the Scrum Master is frequently concerned about what the Scrum Master should expect from the team.
For example, one manager may prefer incremental progress, whereas another seeks integrated teamwork, and a third prefers issue solving.
The solution:
Clear communication is essential for establishing expectations. So, keep engaging your immediate manager to determine what you need to attain in this role.
15. Quickly Solve Challenges
When a problem exists, the Scrum Master is responsible for resolving it as soon as reasonable. However, there could be times when the frequency and size of difficulties make finding quick answers difficult.
The solution:
You may establish a trusting relationship and communication by promoting a culture of high commitment within the team. You may make it simple with the help of the complete team.
16. Space Limitations
A team that does not have a separate meeting place is unlikely to collaborate effectively. Due to meetings workspaces are often over occupied. But when they don’t have the workspace, then they require to decline.
The solution:
Every team must have a designated area to would get together meetups, as well as to connect among each other throughout the day and as required, for Agile to work properly.
17. Not Attending Meetings
Agile meetings are a vital part of the structure, and they must be performed according to the guidelines outlined in the rule books. If meetings are cancelled or delayed due to an unexpected, a team that does not have a separate community centre is unlikely to work.
The solution:
They must be serious about keeping meetings on schedule and ensures that they remain focused and do not exceed the required time.
18. Product Owners Who Aren’t Available
Daily meetings are to frequent for the PO’s. This leads to a lot of uncertainty and a lot of modification, which makes the team lose trust in the agile approach.
The solution:
Work can move along smoothly when the Scrum Master and Product Owner have a close connection. Product owners make it clear that missing a meeting or absence is not an option.
19. Operating with Different Teams
The Agile team has lost targeted guidance and accessible to the Scrum Master when firms hire part-time Scrum Masters or ask one Scrum Master to work on multiple teams at the same time.
In these situations, the Scrum Master also has to promote and realize the team’s highest performance.
The solution:
Part-time scrum masters who over works for economic growth. They also need the additional opportunities to focus on.
Alternatively, instead of working on various teams, spend the majority of your time to one that has a replacement Scrum Master on either team who can take up your responsibilities while you are unavailable.
20. Managing Constraints
There are always limits to the development’s easy execution, and the Scrum Master may find it really difficult to handle so much tension at once! People’s attitudes, growing disagreements, a confusion on needs, or even a lack of the proper resources and devices are all examples of constraints.
The solution:
To overcome these limitations, the Scrum Master must seek the assistance of a sponsorship or a member of the leadership team. Create a list of something like the limitations and come up with ways to get round them.
As Windows Development Company, we also provide Windows App Development services, please check them out as well.
1. Explain the drawbacks of implementing Scrum?
- A scrum master with much less knowledge can allow the project team to dissolve
- Despite of well identified activities there are many inconsistencies.
- It performs great for small organizations and is hard to handle to wider, more complicated tasks
- Requires people with experience
- Teams must be highly interactive and intended to ensure results
- With less knowledge can cause the project to dissolve
2. What exactly could a Scrum Master do?
They enforce the previously agreed agile standards and methods.
This position’s responsibilities include:
- Getting rid of blockages.
- Keeping the team safe from outside shocks and distractions.
3. What are the three Cs of user requirements?
The 3 C’s of User Requirements try and keep the objective of the customer experience in mind, whether you’re a beginner or a friendly person.
- The first C is indeed the Checklist, which is the user story in its most basic form. To keep user requirements simple, they are individually written on indexing “boards.” There are three essential components to the standardized way: As a [user type], I prefer / require [objective] in order to achieve [clarification value]. The Card serves only as a reference.
- The Discussion about the Card is second C. The conversation encourages the agile team to work together in small steps to develop a shared understanding of the issue and possible solutions.
- The Verification is the third C. Verification is the acceptability criterion that collects the necessary requirements and transforms them into specifications so that we can determine when the user narrative has been provided successfully.
4. Is it necessary for a Scrum Master to have technical skills?
Requirement of technical skills are optional for scrum master. The Scrum Master is in charge of identifying and encouraging Scrum in keeping with the Scrum Guide.
They assist everyone in understanding Scrum theory, practices, principles, and values.
5. Is it possible for a Scrum Master to generate user requirements?
Scrum should not have user requirements. Furthermore, the Agile Methodology makes no reference of user requirements or who is responsible for writing them. There are some agile concepts that have stood the test of time.
6. What exactly does Scrum Masters perform throughout the day?
The Scrum Master is in charge of regular Scrums, Scrum meetings, Scrum reviews, and Scrum walkthroughs. To be a Scrum Master also entails clearing hurdles. I teach the team how to address issues under their own, however if required, I would go in and support them in resolving the challenges.
7. When Scrum Master is effective?
They support the Scrum Qualities of Acceptance, Attention, Honor, Dedication, Courage and so does the entire group. They are still ideals to everyone with whom you interact.
8. Is it possible for a Scrum Master to execute the project?
They are senior managers who must possess specific project planning skills such as leadership and attention to details.
It can be termed project managers under this way. Many project management job specifications require scrum expertise.
9. How so many times may the project schedule be transformed in scrum?
This Group decided how and when to improve the product. Refinement includes the integration not more than 10% of total of the Production Team’s capability. On the other hand, Product manager can modify the user stories at any time when needed.
10. What is the maximum number of projects a Scrum Master can manage?
In general, a skilful Scrum Master can essentially work with two to three teams. This generalization, however, comes with a few exceptions.
11. In a scrum, how so many individuals should be present?
A Scrum team typically consists of three to nine members. Scrum operations grow by professional teams among organizations, but rather by having a very large staff. Scrum has capacity for holding the projects which consists of more than 1,000 workers.
Have some time? Visit our Website, LinkedIn page to know more.



